How-To: Create docker container for remote VS Code development
Background
Let’s say that you have a linux server running that you want to setup remote development on. Docker can be used to provide the usual benefits (access control, reproducible environments, etc).
Prerequisites
This assumes an already existing Docker installation on the server and VS Code installation on the local PC.
Container creation
First off, access the server (ssh or physically).
Make a folder for creating the docker image. Let’s also make projects directory while we’re at it.
mkdir projects
mkdir ubuntu-ssh
cd ubuntu-ssh
nano Dockerfile
Insert the following into the Dockerfile.
FROM ubuntu:noble
RUN apt update && apt install openssh-server sudo -y
RUN echo 'ubuntu:defaultpw' | chpasswd
RUN service ssh start
EXPOSE 22
CMD ["/usr/sbin/sshd","-D"]
This sets up a minimal ubuntu docker image with ssh access. User is ubuntu and password is defaultpw. The password can be changed on first access if desired.
Run the command.
docker build -t ubuntu-ssh .
Now that the image is created, we want to create the docker compose file and create the container.
nano compose.yaml
Insert the following into the compose file. Be mindful to replace /path/to/projects with the real path to the projects folder we created earlier.
services:
code-server:
image: ubuntu-ssh:latest
container_name: ubuntu-ssh
volumes:
- /path/to/projects:/projects
ports:
- 2222:22
restart: unless-stopped
Start the container in the background.
docker compose up -d
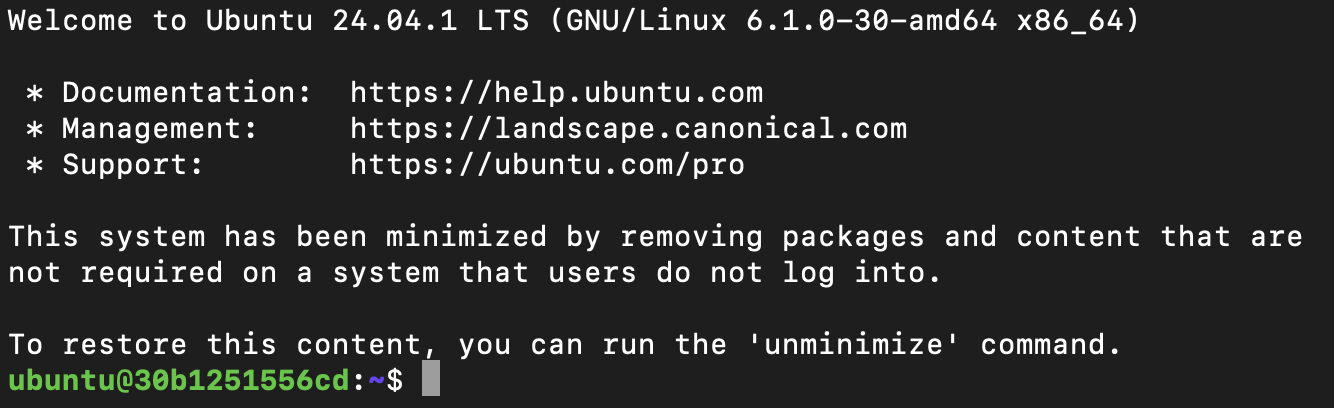
At this point test the ssh connection from the local PC to the container.
ssh ubuntu@serverip -p 2222
Connect with VS Code
On your local PC, install the Remote - SSH extension.
With the VS Code extension connect using ssh to the running container. Navigate to the projects folder where you persistant files will be saved.
From this point, if you open a terminal in VS Code, it will be a terminal running on the container. You can then install any needed packages for development (gcc, python, etc.). In fact, it is a good idea to document everything that is installed so that you can quickly restore the environment if the container is recreated.
You created this image, so you need to keep it updated. Occasionaly run sudo apt update and sudo apt upgrade to update the packages.